Login to leave a comment.
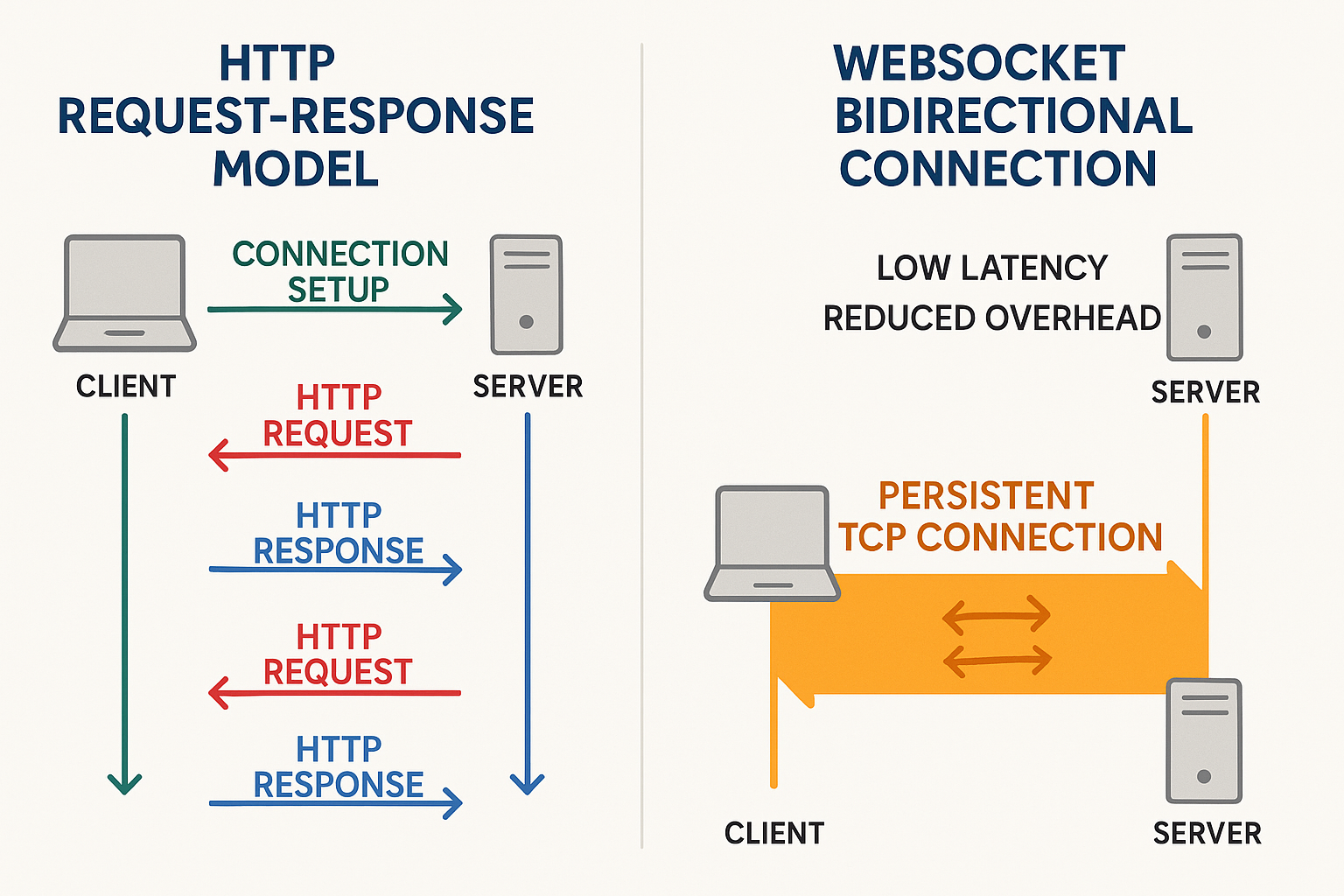
In our hyper-connected world, users expect real-time responsiveness from apps—whether that’s live chat, gaming, financial updates, or collaborative editing. WebSockets shine in this arena, offering a full‑duplex, persistent connection over a single TCP channel. Once the initial handshake upgrades the HTTP connection (HTTP 101), both client and server can send messages anytime, eliminating the latency of repeated HTTP requests.
Why Choose WebSockets in 2025?
-
Real-time interactivity: Ideal for applications like chat, live feeds, and games.
-
Efficiency: Reduces bandwidth and header overhead.
-
Bidirectional flow: Both client and server can initiate messages.
-
Broad adoption: Fully standardized and supported across platforms.
How WebSockets Work
-
Handshake: Client sends an HTTP GET with 'Upgrade: websocket' headers.
-
Server upgrades: Responds with status 101 and confirmation header.
-
Persistent Connection: A single TCP socket remains open.
-
Full-duplex messaging: Both sides exchange data until closure.
Implementation Highlights
Frontend (JavaScript):
const socket = new WebSocket('wss://yourserver.com/socket');
socket.onopen = () => console.log('Connected');
socket.onmessage = (e) => console.log('Server:', e.data);
socket.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'ping' }));
Backend (Node.js):
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8080 });
wss.on('connection', ws => {
ws.on('message', msg => ws.send(`Echo: ${msg}`));
});
Security & Scalability Best Practices
-
Use wss:// and TLS to encrypt data.
-
Validate 'Origin' headers to prevent CSWSH.
-
Use tokens and scoped cookies for auth.
-
Use Redis or message brokers to scale.
Conclusion
WebSockets empower real-time, low-latency web experiences. Implementing them securely and efficiently ensures your applications are future-ready.
0 comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!